Biopsy Testing Centre
Biopsy Testing Centre in Jaipur — Accurate, Image-Guided Biopsy Testing
When a physician notices an unusual lump, swelling, or tissue growth, the only most reliable means of determining the true nature of the findings often boils down to a single procedure: a biopsy. While the term biopsy strikes fear into the hearts of many, the procedure itself is actually a form of diagnostic testing, which removes all doubt. A biopsy will facilitate the determination of whether a lesion is benign, inflammatory, infectious, or malignant, and will even prescribe the treatment pathway with crystal clarity. When you are looking for a Biopsy Testing Centre in Jaipur, you are looking for a facility which can ideally perform the procedure with accurate samples, with imaging guidance where indicated, with complete sterility, and with a patient-friendly process. While a biopsy refers specifically to the procedure of collecting a sample, collecting the right sample, at the right location, with the utmost care possible, biopsies are rapidly being replaced by imaging-guided techniques, which not only locate the exact target but strike it with unerring accuracy via the precise use of ultrasound, computerized tomography, or fluoroscopy. This form of biopsy testing can be recommended in the case of a thyroid nodule, a breast lump, a swollen lymph node, a liver lesion, a pulmonary mass, a bone lesion, a kidney issue, or any suspected lesion.
What is Biopsy Testing?
Biopsy testing is a medical procedure whereby tissue or cell samples are removed from the body for microscopic analysis in a lab. This microscopic examination leads to positive identification of the test result. Biopsy testing is usually advised when there are imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT, MRI, or X-ray, of an abnormal area in the body, which can’t be diagnosed without tissue validation.
In most instances, biopsy testing assists with:
- verify whether a tumor is benign or malignant
- identify infection or inflammation
- determine the type and grade of cancer (if present)
- An individual guide on the right treatment option, whether medicine, surgery, ablation, embolization, or oncology, without having too many surgeries if the lesion is benign. Patients are usually confusing a biopsy with surgery, but modern biopsies are actually a minimally painful process involving only a needle. This can usually be carried out under local anesthetic, with a quick turnaround time, especially with image guidance.
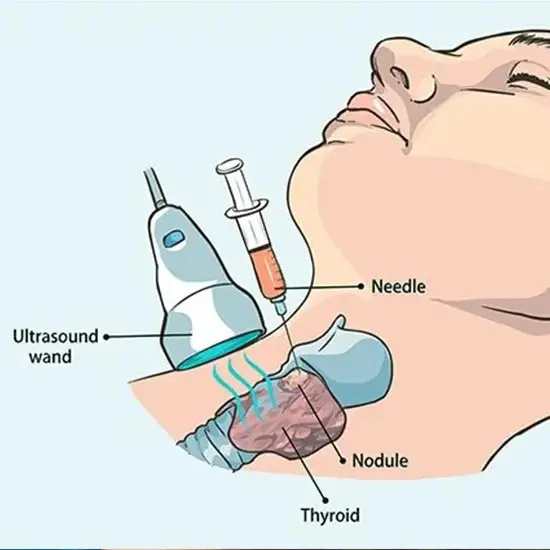
Types of Biopsy (Complete Guide)
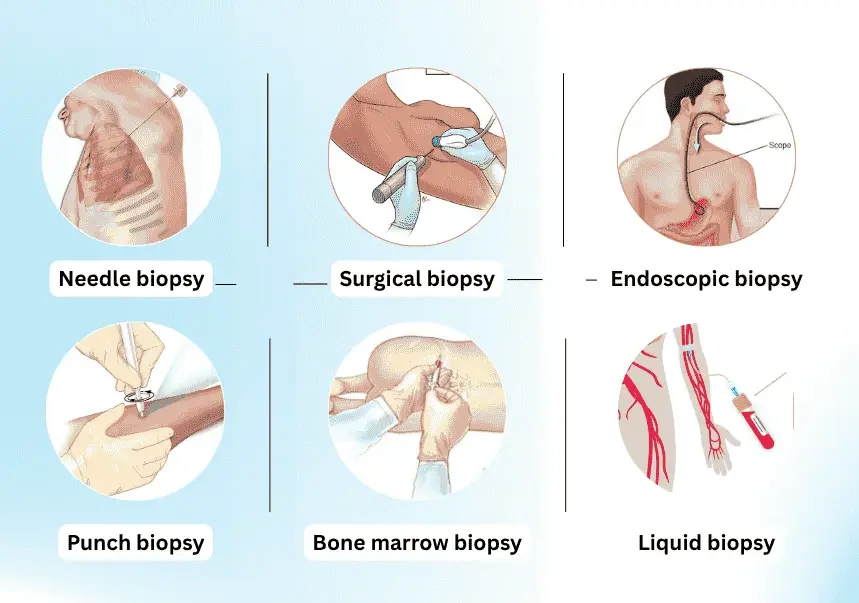
Biopsies vary in types, which are selected based on the positioning of the lesion, its size, and the information that needs to be confirmed. Some of the most popular biopsy types are given here:
1) FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology):
A thin needle removes cells from a mass to be examined.
FNAC stands for “Fine Needle
It is commonly used for:
- thyroid nodules
- lymph nodes
- breast lumps (in selected cases)
- In cases involving lumps in the superficial soft tissue,
FNAC Testing is a rapid procedure which requires little preparation. It can be carried out either with or without ultrasound guidance, depending on the level of the lump. In FNAC, a diagnosis based on cell characteristics—cytology—is obtained, and there is no view of tissue architecture.
2) Then comes Core Needle Biopsy (Tru-Cut Biopsy).
In this procedure, a slightly thicker needle is employed to remove a small amount of tissue rather than cells alone. A larger amount of information is generated with this technique, and it is employed for:
- breast masses
- lymph nodes
- liver lesions
- soft tissue tumors
- prostate-related lesions (as advised by specialist)
- kidney lesions (case-dependent)
Core biopsy is very useful in that it preserves the tissue architecture, thereby increasing the sensitivity of the test beyond FNAC in most cases.
3) Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy
Ultrasound-guided biopsy is not another form of biopsy, but it is one of the guidance tools. Extremely popular owing to its safety, toxicity, radioactive, and one-stage visualization, it is used in:
- thyroid biopsy
- breast biopsy
- lymph node biopsy
- liver and abdominal lesions
- superficial masses and collections
Ultrasound guidance has the tendency to enhance accuracy while reducing patient discomfort and the time taken for the procedure.
4) CT-Guided Biopsy
A CT-guided biopsy is generally selected for lesions that are deep or otherwise difficult to visualize by ultrasound.
This includes:
- Lung nodules/masses
- Deep abdominal or pelvic masses
- Bone lesions, where selected
- Deep lymph nodes
CT guidance allows the clinician to very precisely and safely target lesions that are difficult or impossible to approach by traditional means.
5) Stereotactic Biopsy (Breast Biopsy)
Some breast lesions are better visualized in mammography than in ultrasound.Stereotactic biopsy uses mammogram-based guidance to sample such lesions. It is often advised for calcifications or specific breast changes.
6) Endoscopic Biopsy (GI Tract) :
If the abnormality lies in the gastrointestinal tract, a biopsy can be obtained through endoscopy or colonoscopy. The specialist who performs this type of task is a gastroenterologist.
7) Surgical Biopsy (Excisional/Incisional):
In certain situations, a surgeon might recommend a comprehensive biopsy in situations where.
- the lesion cannot be safely sampled by needle
- the lump needs complete removal Results from
- needle biopsy may be noncontributory even when the index of suspicion remains high.
When this is so, a surgical biopsy may be indicated since this method is more invasive than a needle biopsy.
Why choose Biopsy Testing Centre in Jaipur?
There is no standard biopsy. Some lumps can easily be palpated and biopsied, while there are lesions that exist in deep, hidden, and small locations close to essential structures. Here, image-guidance technology is needed to guarantee:
- accurate needle placement into the lesion
- better sample quality and diagnostic accuracy
- reduced risk of injury to nearby organs or vessels
A good biopsies program in Jaipur should make the need for repeat biopsies be less, by ensuring image guided biopsies, step by step, from pre-biopsy through the procedure, through the follow-ups.
What is the process involved in the biopsies test?
The most modern procedures follow this step by step:
the doctor examines your image test, whether it is ultrasonography, CT scans, or MRI, in order to decide which kind of biopsies need to be done. There might be a few procedures that need to be accomplished prior to the test, mostly blood testing, which will involve the risks of bleeding, especially in core biopsies. On the actual day of the test, the region will be cleaned and disinfected. Local anesthesia will be involved, making the patient comfortable throughout the majority of the test. After sampling, a bandage is applied and you may be observed briefly. Usually, patients go home on the same day. This sample will then be sent to the pathology lab to be evaluated by examination using a microscope and additional tests when necessary.
How to Prepare for Biopsy Testing Centre in Jaipur
Before the Although preparation varies according to the type of biopsies to be done, some of the most basic and necessary
- Notifying your physician if you are taking blood thinners (aspirin, clopidogrel, warfarin,
- Sharing any history of bleeding disorders
- Providing existing imaging reports and medical records
- Following fasting instructions if advised (especially for certain deep biopsies)
- Arranging one accompanying person for convenience Signing a consent form after understanding the procedure Never stop blood thinners on your own—always follow medical guidance.
Is Biopsy Testing Safe?
Usually, this is true, provided that experts perform this task using aseptic methods and imaging guidance. You may experience some pain or soreness, perhaps more in core biopsy, but rarely will complications occur once safety measures are in place.
These may include:
– Mild pain or tenderness at the site of the biopsy
– small bruise or swelling
– Minor Bleeding (which is normally easy to stop)
• There is a risk of infection, although this is rare, and can be minimized through the use of sterile technique. Additionally, for the more tertiary biopsies, such as the lung, liver, or bone, the issue of safety is much more important.
Common Areas where Biopsy Tests are Performed
Provided below are
A one-step Biopsy Testing Centre can adequately handle biopsies from:
- Thyroid nodules (FNAC or core biopsy, if required)
- Mammary nodule (core biopsy or FNAC, according to case)
- Lymph node enlargement (FNAC or Core Biopsy)
- Liver masses (Ultrasound/CT-guided core biopsy
- Lung Nodules (CT Guided Bi
- Renal lesions (case-by-case
- Soft tissue masses (FNAC or Core biopsy)
- Bone lesions (requiring special guidance when needed)
The choice of biopsy depends upon which organ is affected and which diagnosis is required to be confirmed.
After Biopsy: Recovery and Care
Most needle biopsies allow quick recovery. Patients are often advised:
- keep the dressing clean and dry for a short period
- avoid heavy exercise for a short time if advised
- watch for unusual swelling, persistent bleeding, fever, or severe pain
- return for follow-up or report review
The recovery timeline varies by biopsy location. Superficial biopsies usually heal quickly. Deep biopsies may require slightly longer rest or monitoring.
Why a Dedicated Biopsy Testing Centre in Jaipur Matters
Choosing the right center improves diagnosis accuracy and reduces repeat procedures. A good biopsy Centre typically provides:
- imaging-guided targeting for better precision
- safe sterile technique
- proper pre-biopsy evaluation (including bleeding risk checks)
- experienced doctors and support staff
- clear after-care instructions
- coordination for pathology reporting and follow-up
And accuracy is very important, since an accurate diagnosis will open the doors not only to proper treatment, but also to save you from the ordeal of surgery or taking medication for months.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What is biopsy testing?
This is the process by which a sample of tissue or cells is extracted from the body with the intention of viewing the cells under a microscope with a view to establishing a diagnosis.
2) In every case of cancer, will biopsy be performed?
No. Biopsy assists in the diagnosis of several conditions, like benign tumors, infection, inflammation, and malignancy.
3) What kinds of biopsies are available through testing?
These may involve FNAC, core needle biopsies (Tru-cut biopsies), ultrasound biopsies, CT biopsies, stereotactic biopsies, endoscopic
4) What is the difference between FNAC and core biopsy?
FNAC involves a thin needle for cellular extraction, whilst a core biopsy involves a tiny tissue excision for precise structural detail.
5) Is biopsy testing painful?
Pain is usually not present since biopsies are usually conducted under local anesthesia. Pressures experienced are not significant.
6) Biopsy time: Needle biopsies are often short,
but the time involved can depend on factors related to the position of the lesions being biopsied and the modality used to guide the procedure and any needed recovery time.
7) Must I fast before having a biopsy?
Fasting depends on biopsy type. Some deep biopsies may require fasting, while many superficial biopsies do not.
8) Can I take blood thinners before biopsy?
You must inform the doctor. Some blood thinners may require an adjustment before the biopsy, but this should only be under a physician’s care.
9) When should I expect biopsy results?
This will depend because some places test samples faster than others, and there might be additional testing to determine the best diagnosis.
10) Are there complications with biopsy testing?
These will, for the most part, be very ordinary—the kind you get from bruising or light bleeding. There will not be many serious reactions unless it is not performed properly.
11) How do I proceed after the biopsy?
Expect observation, guidance, and then another appointment to determine the course of treatment based on the biopsy results.
12) Could I do this again?
Yes. There will be times when the first biopsy did not provide enough information, and another is recommended, though with proper direction, this should not be the case.
